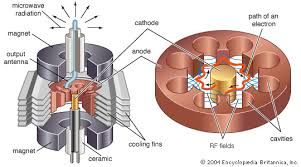
Microwave & Millimetrewave Power Devices
Xiaodong Chen and Yasir Alfadhl
Microwave/Millimetre Wave Power Devices refer to the generators and amplifiers operating in microwave and millimetre wave bands. These power devices are widely applied in communication, radar, imaging, industrial heating, particle accelerators, plasma diagnostics, electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) and fusion energy, and etc. We are working on two types of microwave and millimetre wave power devices: vacuum electronic devices and solid-state devices.
Vacuum Electronic Devices
Vacuum electron devices (VEDs) are the most powerful and efficient sources of coherent radiation throughout the microwave and millimeter wave bands. Our recent work on vacuum electronic devices has been focusing on millimetre wave bands, including Extended Interaction Klystron Oscillators (EIKO) and Backwave Oscillators (BWO) using pseudospark (PS)-sourced sheet electron beam; and spatial harmonic magnetrons and rising sun anode magnetrons; and high spatial harmonic gyrotrons.
Pseduospark electron beam devices – EKIOs and BWOs
To overcome the limitation of conventional thermionic cathode, the pseduospark(PS) electron beam driven EIKOs and BWOs have been investigated under two EPSRC funded projects, in collaboration with University of Strathclyde. The configuration of PS electron beam driven devices are shown in the figures below. These devices are characterised by high power, low cost, and compactness without the need of the magnetic focusing system.
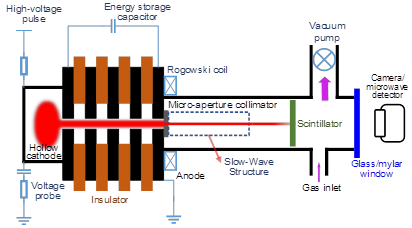
Figure 1: Experimental set-up of PS electron beam driven devices
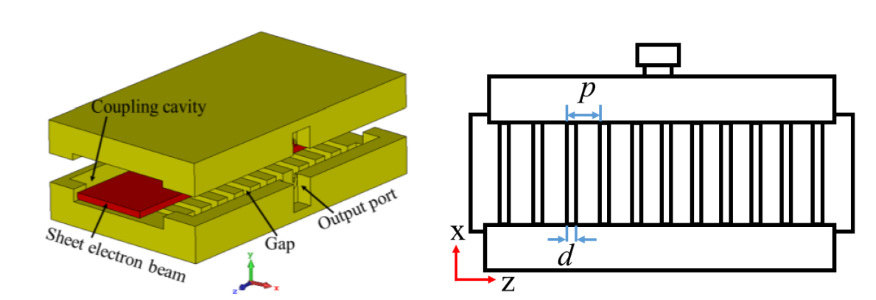
Figure 2: Schematic drawing of the EIKO SWS operating at 352GHz
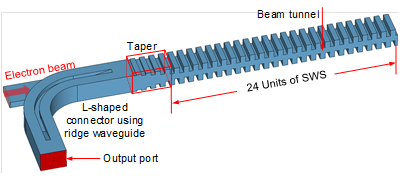
Figure 3: Structure of the double staggered grating SWS BWO operating in the range of 343-381 GHz
Millimetre wave magnetrons
Based on our extensive experience in microwave magnetrons, we have extended the operating frequency of magnetron to W-band, by employing either spatial harmonic anode or rising-sun anode. Figures below show the structures of these magnetrons.
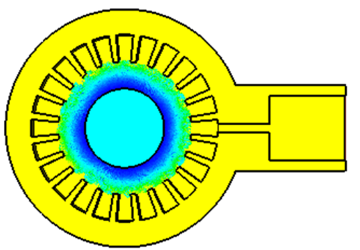
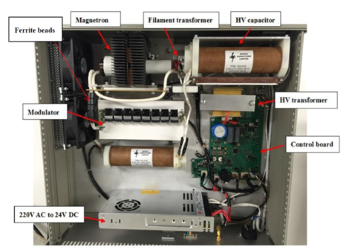
Figure 4: The W-band Spatial Harmonic Magnetron: the cavity and the magnetron system
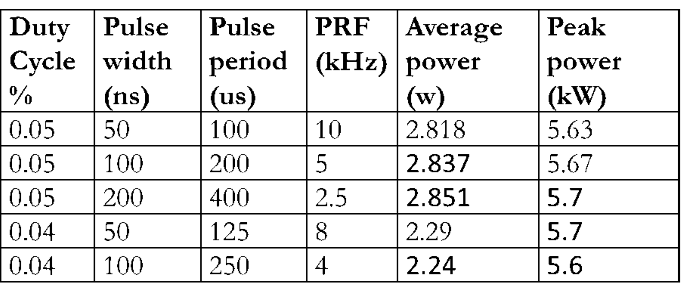
Table 1: W-band spatial harmonic magnetron performance
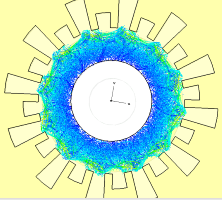
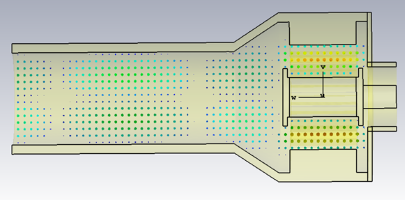
Figure 5: W-band Rising-sun anode magnetron: the cross and axial views
Gyrotron-Multiplifer
Gyrotron is a typical fast wave device which can be used as an amplifier or oscillator. As shown below, it consists of an electron gun with input and output cavities along the axis of the electron beam. It usually has a solenoidal bias magnet that provides an axial magnetic field. This field forces the electrons to travel in tight spirals down the length of the tube.
We have designed a gyrotron-multiplier operating in 1.3THz in collaboration with University of Strathclyde.
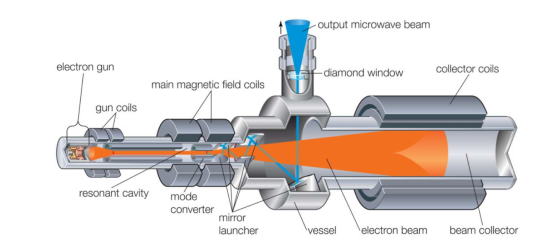
Figure 6: Schematic of a gyrotron
Solid state power devices
Lately, we have started to work on solid state power devices based on diamonds in collaboration with Leicester University. Diamond is a unique material and has a potential for much high power electron device applications. Looking at any comparative table of physical properties and the reasons are obvious.
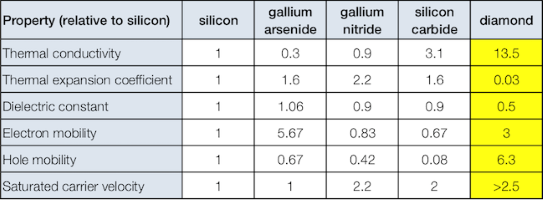
Table 2
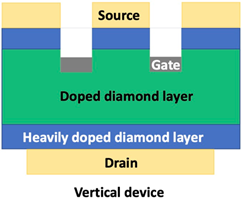
We are developing a vertical diamond Field Emission Transistor(FET) for fast high voltage switching as show below.
Highlights and Research Outcomes
We organised and hosted the EPSRC-funded National Vacuum Electronics Conference (NVEC) 2020 on 19th November, 2020.
We hosted 12th IEEE UK-Europe-China Workshop on Millimeter Waves and Terahertz Technologies (UCMMT) in London, UK, 20-22 August, 2019. Antennas & Electromagnetics Research Group :: UCMMT 2019 in London organised by QMUL
Selected Research Grants and Projects:
- EPSRC Research Grant: SHeet Electron beam vacuum electronic Devices for the Generation of High power THz radiation (SHED_LIGHT_THz), Grant No. - EP/S00968X/1 & EP/S009582/1. Starts: March 2019, Ends: August 201, Value: £245k;
- Chinese Scholar Council (CSC) Scholarship: ‘Advanced vacuum electronic devices’, January, 2019-Jnuary,2020;
- CSC-QMUL Studentship: ‘THz gyrotron-Multiplier’, September, 2012 – May, 2016
- CSC-QMUL Studentship: ‘Millimetre wave magnetrons’, September, 2011- September, 2015
- EPSRC Research Grant: Generation of high power, high frequency radiation using high brightness pseudospark-sourced relativistic electron beams” (Nov. 2008 – April, 2014, EP/E058868/1 and EP/G012490/1), Value: £240k.
Selected Recent Publications
Journal papers:
- Zhang, J., Zhang, T., Alfadhl, Y., Chen, X., Zhang, L., Yin, H., & Cross, A. W. (2020). Study on Wideband THz Backward Wave Oscillator Driven by Pseudospark-Sourced Sheet Electron Beam. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 67(8), 3395-3402. doi:10.1109/ted.2020.3005362
- Zheng, Y., Zhang, R., Chen, X., Hing, P., Liu, J., Wei, J., . . . Ye, H. (2020). Doomed Couple of Diamond with Terahertz Frequency: Hyperfine Quality Discrimination and Complex Dielectric Responses of Diamond in the Terahertz Waveband. ACS Applied Electronic Materials, 2(5), 1459-1469. doi:10.1021/acsaelm.0c00216
- Yin, H., Zhang, L., Xie, J., Ronald, K., He, W., Shu, G., . . . Cross, A. W. (2019). Compact high-power millimetre wave sources driven by pseudospark-sourced electron beams. In IET Microwaves, Antennas and Propagation Vol. 13 (pp. 1794-1798). doi:10.1049/iet-map.2018.6190
- Xie, J., Yuan, X., Meng, L., Cross, A. W., Zhang, L., Yin, H., . . . Alfadhl, Y. (2020). Study of a 0.35 THz Extended Interaction Oscillator Driven by a Pseudospark-Sourced Sheet Electron Beam. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 67(2), 652-658. doi:10.1109/TED.2019.2957760
- Duan, Z., Tang, X., Wang, Z., Zhang, Y., Chen, X., Chen, M., & Gong, Y. (2017). Observation of the reversed Cherenkov radiation, Nature Communication, 8, 14901. doi:10.1038/ncomms14901
- Li, X., Liu, X., Ronald, K., He, W., Zeng, Y., Alfadhl, Y., . . . Chen, X. (2017). Investigation of Frequency-Selective Surfaces for a THz Gyromultiplier Output System. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 64(11), 4678-4685. doi:10.1109/TED.2017.2746718
- LI, X., Liu, X., Alfadhl, Y. A. S. I. R., Ronald, K., He, W., Cross, A., & Chen, X. (2016). A Dual-Frequency Quasi-Optical Output System for a THz Gyro-Multiplier. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology. doi:10.1109/TTHZ.2016.2581982
- Li, X., Lang, J., Alfadhl, Y., & Chen, X. (2015). Study of an eighth-harmonic large-orbit gyrotron in the terahertz band. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 43(2), 506-514. doi:10.1109/TPS.2014.2384200
- Li, X., Lang, J., Alfadhl, Y., & Chen, X. (2015). Study of an eighth-harmonic large-orbit gyrotron in the terahertz band. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 43(2), 506-514. doi:10.1109/TPS.2014.2384200
Conference papers:
- Jin Zhang, Huabi Yin, Tianzhong Zhang, Yasir Alfadhl, Xiaodong Chen*, Adrian Cross, Wenlong He and Jie Xie, "Design of 0.365-THz Backward Wave Oscillator using Staggered Double Grating SWS and Sheet Beam," 2019 12th IEEE UK-Europe-China Workshop on Millimeter Waves and Terahertz Technologies (UCMMT), London, UK, 2019, pp. 1-3.
- T. Zhang, J. Zhang, J. Lang and X. Chen, "Experimental Testing of a W-band spatial harmonic magnetron," 2019 12th UK-Europe-China Workshop on Millimeter Waves and Terahertz Technologies (UCMMT), London, UK, 2019, pp. 1-3, doi: 10.1109/UCMMT47867.2019.9008359.
- Lang, J., Chen, X., & IEEE. (2017). Investigation of a 210GHz Spatial Harmonic Magnetron using 3-D Particle-in-Cell Simulation. In 2017 EIGHTEENTH INTERNATIONAL VACUUM ELECTRONICS CONFERENCE (IVEC). Retrieved from http://gateway.webofknowledge.com/gateway/Gateway.cgi?GWVersion=2&SrcApp=PARTNER_APP&SrcAuth=LinksAMR&KeyUT=WOS:000427399500059&DestLinkType=FullRecord&DestApp=ALL_WOS&UsrCustomerID=612ae0d773dcbdba3046f6df545e9f6a
- Cross, A. W., Yin, H., He, W., Zhang, L., Ronald, K., Phelps, A. D. R., . . . Zhao, J. (2017). W-band extended interaction oscillations using post-accelerated pseudospark-sourced electron beams. In 2017 10th UK-Europe-China Workshop on Millimetre Waves and Terahertz Technologies, UCMMT 2017. doi:10.1109/UCMMT.2017.8068484
- Lang, J., Alfadhl, Y., & Chen, X. (2017). Investigation of a 95 GHz spatial harmonic magnetron for cloud radar. In Proceedings of IEEE 9th UK-Europe-China Workshop on Millimetre Waves and Terahertz Technologies, UCMMT 2016 (pp. 74-75). doi:10.1109/UCMMT.2016.7873966
- Cross, A. W., He, W., Zhang, L., Yin, H., Bowes, D., Ronald, K., . . . Zhao, J. (2017). Compact sub-terahertz radiation sources driven by pseudospark-produced electron beams. In Proceedings of IEEE 9th UK-Europe-China Workshop on Millimetre Waves and Terahertz Technologies, UCMMT 2016 (pp. 69-71). doi:10.1109/UCMMT.2016.7873964
- Li, X., Lang, J., Alfadhl, Y., & Chen, X. (2013). MAGIC 3D simulation of starting oscillation process in a 42 GHz gyrotron. IET Seminar Digest, 2013(4), 27-28. doi:10.1049/ic.2013.0245
- Xiang Li, Jiandong Lang, Yasir Alfadhl and Xiaodong Chen. ‘Study of starting process of oscillation in a gyrotron using 3D PIC simulation’, National Vacuum Electronic Conference 2013. London, UK, June 2013.
- Jiandong Lang, Xiang Li, Yasir Alfadhl and Xiaodong Chen. ‘3D spatial harmonic magnetron-a contender for compact high power THz source’, National Vacuum Electronic Conference 2013. London, UK, June 2013.